
2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者血清脂联素.pdf

qw****27



在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者血清脂联素.pdf
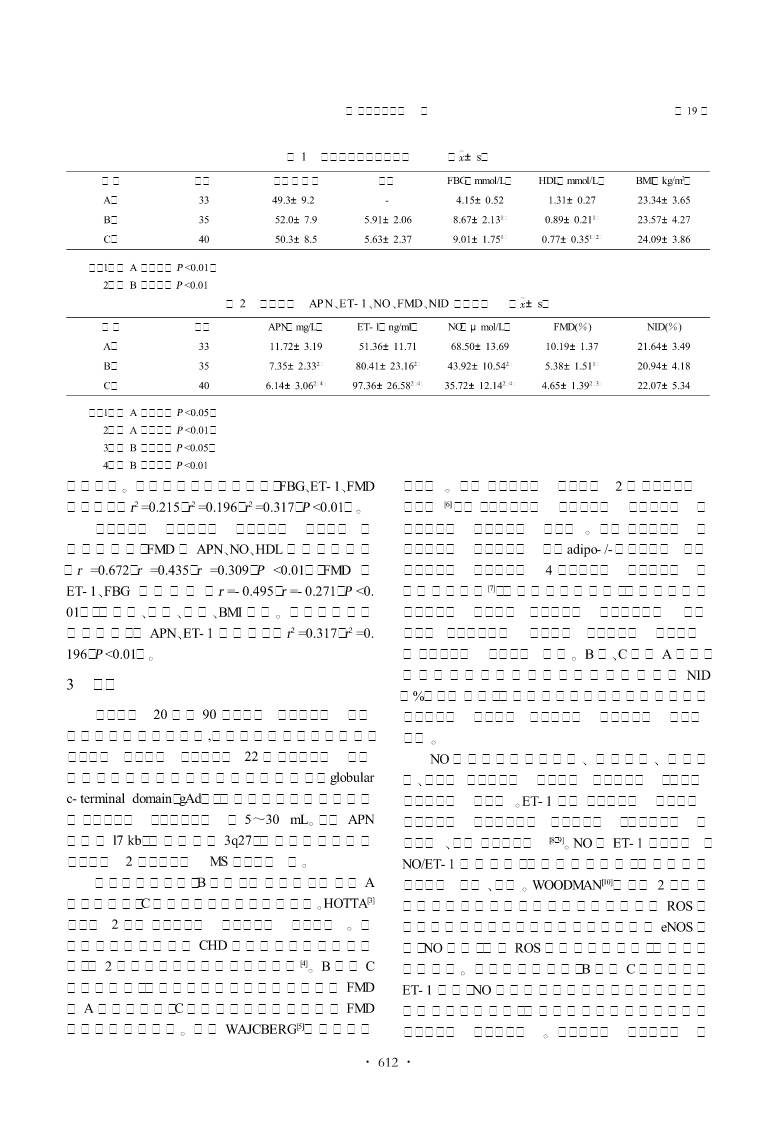
第19卷第4期中国现代医学杂志Vol.19No.42009年2月ChinaJournalofModernMedicineFeb.2009文章编号:1005-8982(2009)04-0610-042型糖尿病合并冠心病患者血清脂联素、血皮素-1和一氧化碳与血管内皮功能相关性研究张霞,侯明辉,孟杰,尹玲(河北大学附属医院内分泌科,河北保定071000)摘要:目的研究糖尿病合并冠心病患者血清脂联素(APN)、一氧化氮(NO)、内皮素(ET-1)、高密度脂蛋白(HDL)、反应性充血肱动脉内径增加程度(FMD)的水

2型糖尿病并冠心病患者血清脂联素水平测定.pdf
JournalofZhengzhouUniversity(MedicalSciences)Nov.2008Vo1.43No.6·1l95·[3]李洁,周灿权,钟依平,等.低剂量GnRHa在IVF—ET中的[7]BormG,MannaertsB.Treatmentwiththegonadotrophin—re—应用之三长效1.3mgGnRHa与短效GnRHa长方降调节leasinghormoneantagonistganirelixinwomenundergoing的比较[J].中华现代妇产科学杂志,200

2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者脂联素测定及其意义.docx
2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者脂联素测定及其意义【摘要】目的研究脂联素与2型糖尿病合并冠心病相关性探讨脂联素与2型糖尿病合并冠心病的作用和机制。方法选择正常对照组48例、2型糖尿病组62例和2型糖尿病合并冠心病组68例测定脂联素、糖化血红蛋白、总胆固醇、甘油三酯、高密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白、空腹血糖、空腹胰岛素进行观察。结果脂联素、胰岛素抵抗指数存在负相关关系脂联素与性别、GHbAlc、FINS、BMI、LDL、TG独立相关。结论脂联素水平的降低与2型糖尿病合并冠心病形

2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者脂联素测定及其意义.docx
2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者脂联素测定及其意义【摘要】目的研究脂联素与2型糖尿病合并冠心病相关性探讨脂联素与2型糖尿病合并冠心病的作用和机制。方法选择正常对照组48例、2型糖尿病组62例和2型糖尿病合并冠心病组68例测定脂联素、糖化血红蛋白、总胆固醇、甘油三酯、高密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白、空腹血糖、空腹胰岛素进行观察。结果脂联素、胰岛素抵抗指数存在负相关关系脂联素与性别、GHbAlc、FINS、BMI、LDL、TG独立相关。结论脂联素水平的降低与2型糖尿病合并冠心病形

2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者脂联素测定及其意义.docx
2型糖尿病合并冠心病患者脂联素测定及其意义【摘要】目的研究脂联素与2型糖尿病合并冠心病相关性探讨脂联素与2型糖尿病合并冠心病的作用和机制。方法选择正常对照组48例、2型糖尿病组62例和2型糖尿病合并冠心病组68例测定脂联素、糖化血红蛋白、总胆固醇、甘油三酯、高密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白、空腹血糖、空腹胰岛素进行观察。结果脂联素、胰岛素抵抗指数存在负相关关系脂联素与性别、GHbAlc、FINS、BMI、LDL、TG独立相关。结论脂联素水平的降低与2型糖尿病合并冠心病形
