
20090817山东特大暴雨雷达回波及地形作用分析.pdf

qw****27





在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

20090817山东特大暴雨雷达回波及地形作用分析.pdf
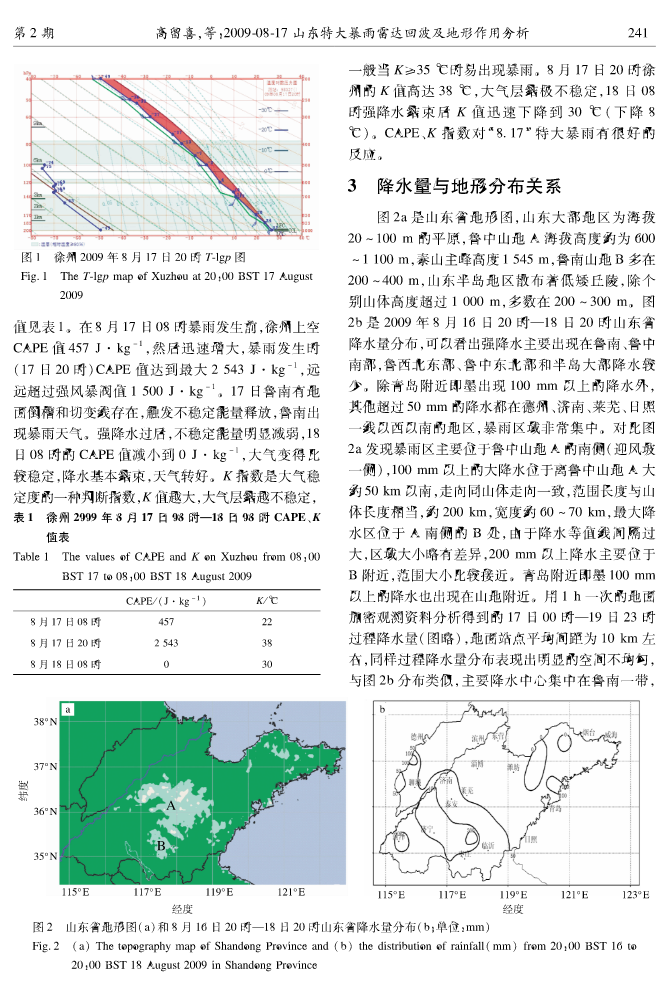
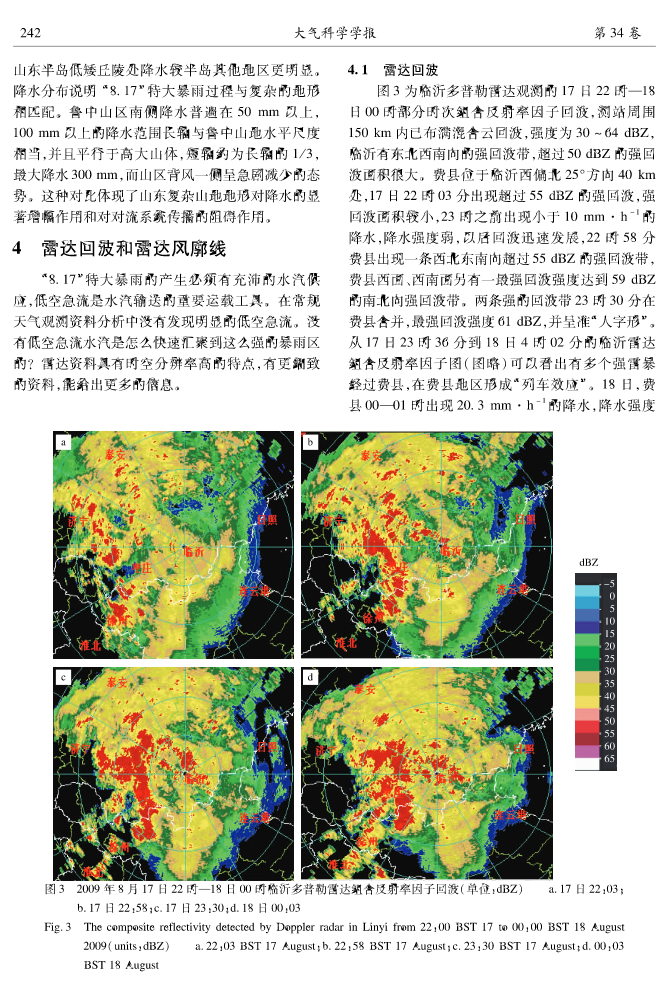
第34卷第2期大气科学学报Vol.34No.22011年4月TransactionsofAtmosphericSciencesApr.2011高留喜,王彦,万明波,等.2011.20090817山东特大暴雨雷达回波及地形作用分析[J].大气科学学报,34(2):239245.GaoLiuxi,WangYan,WanMingbo,etal.2011.AstudyonradarechoandtheimpactofterrainontheheavytorrentialrainfalleventinS

2009-08-17山东特大暴雨雷达回波及地形作用分析.docx
2009-08-17山东特大暴雨雷达回波及地形作用分析2019年8月17日,山东地区遭受了一次特大暴雨袭击,给当地的交通、农业、市政设施等带来了巨大的损失。在这次暴雨中,雷达回波扮演了重要角色。本篇论文旨在探讨山东特大暴雨中雷达回波以及地形对暴雨的影响。一、特大暴雨带来的灾害2019年8月17日,山东地区降下特大暴雨,许多地方出现洪涝灾害、泥石流灾害、山体滑坡等自然灾害。截止8月18日,山东地区共有17名市民失踪,5人遇难,30人受伤。特大暴雨严重影响了当地的交通运输。Sh249线兰陵段、S19济青高速及

“7·12”红安特大暴雨地形作用及雷达回波分析.docx
“7·12”红安特大暴雨地形作用及雷达回波分析近年来,我国的气候异常频繁,特别是地质灾害频发的情况越来越严重。其中,暴雨成为引发地质灾害的主要原因之一。2016年7月12日,发生在湖北省红安县的特大暴雨便是一个典型的例子。本文通过对该次暴雨的地形作用及雷达回波分析,探讨其成因和对控制措施的启示。第一部分:红安县暴雨情况2016年7月12日,红安县遭遇了一场长时间的特大暴雨,期间暴雨降水量高达500毫米以上。这场暴雨引发了较严重的洪涝灾害和山洪灾害,致使该县27个乡镇,1254个村庄,约80万人受灾,308

“7.21”特大暴雨的地形影响分析.docx
“7.21”特大暴雨的地形影响分析“7.21”特大暴雨的地形影响分析摘要:“7.21”特大暴雨是指发生在某个特定时间和地点的持续下雨,造成了极大的洪涝灾害,对地形地貌产生了巨大的影响。本论文将从地形影响的角度出发,深入分析“7.21”特大暴雨的地形影响,重点讨论地形对暴雨洪涝灾害的影响机制和防灾对策。1.引言自然灾害是人类社会发展过程中常常面临的一种巨大威胁,而暴雨洪涝灾害是其中一种严重的自然灾害。地形是暴雨洪涝灾害发生和发展的重要环境因素之一,对洪涝灾害的影响至关重要。因此,对于“7.21”特大暴雨的地

一次阻高背景下地形对晋南特大暴雨的作用分析.docx
一次阻高背景下地形对晋南特大暴雨的作用分析晋南是中国北方一个地势复杂的地区,其地形条件起伏不平,地势高低差异明显,有山峰、河流、湖泊等丰富的自然资源。但是这样的地形条件却经常给当地居民带来危险。特别是在阻高背景下,往往会导致严重的洪涝灾害,而这次特大暴雨也并非例外,为此,本文将尝试从地形的角度来分析高地带来的影响。首先,阻高地区是引起强对流天气的重要地区。阻高是一种大范围的气压场,它不仅能够改变气温和气压,还能引起强湍流,形成强对流天气。在阻高带上空,空气流动异常剧烈,容易形成大规模的锋面、暴雨等天气现象
