
结核分枝杆菌耐药基因检测3.pdf

qw****27


在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

结核分枝杆菌耐药基因检测3.pdf
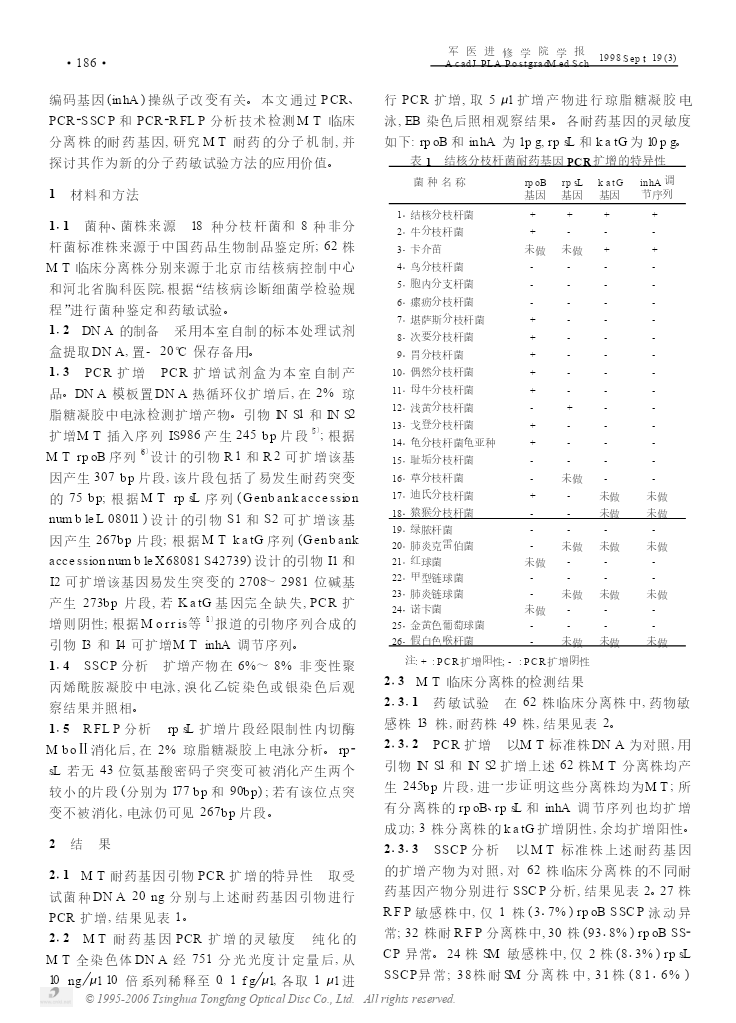
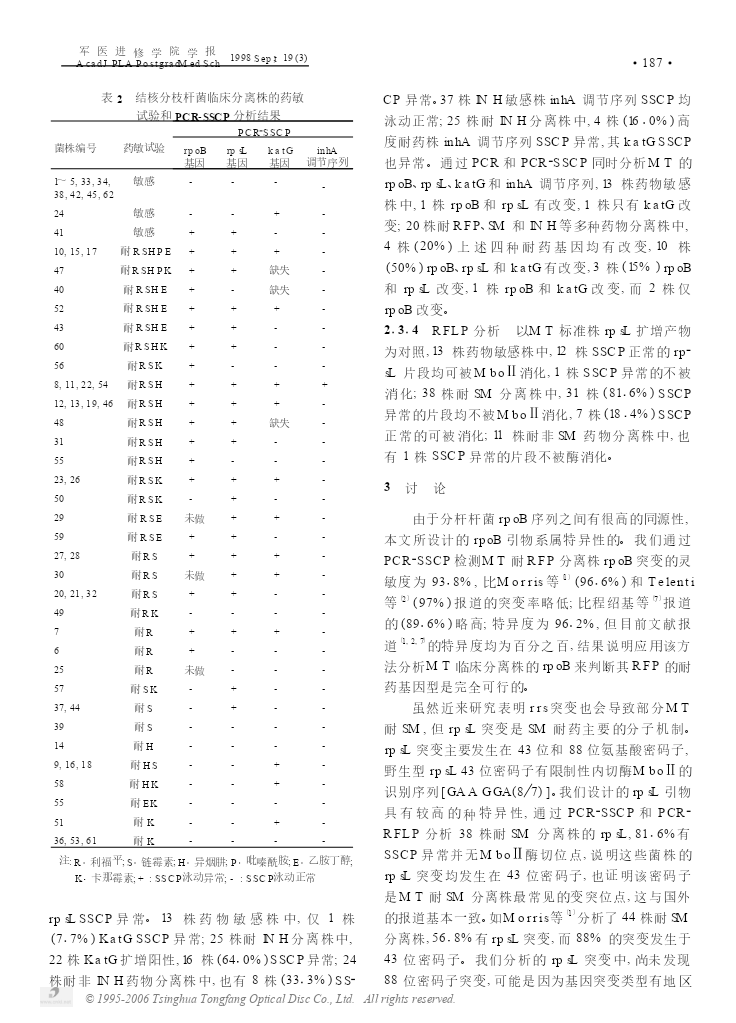
军医进修学院学报1998;19(3)AcadJPLAPostgradMedSchSept·581·结核分枝杆菌耐药基因检测3吴雪琼庄玉辉张俊仙张晓刚何秀云李国利摘要目的:研究结核分枝杆菌(Mycobacteriumtuberculosis,MT)耐药的分子机制,建立快速检测耐药基因型的分子药敏试验方法。方法:通过聚合酶链反应(Polymerasechainreaction,PCR)、PCR2单链构象多态性(Sin2gle2strandedconformationpolymorphism,SSCP)、PCR

结核分枝杆菌常见耐药基因突变的检测与分析.pdf
分类号:R378.91+1密级:一般UDC:616-093编号:2010212554广州医学院硕士学位论文结核分枝杆菌常见耐药基因突变的检测与分析研究生:杨辉导师:吴爱武教授陈心春教授申请学位级别:医学硕士年级:二零一零级学科专业:临床检验诊断学研究方向:感染与免疫论文提交日期:2013年5月论文答辩日期:2013年6月学位类型:医学科学学位学位授予单位:广州医学院答辩委员会主席:评议人:二0一三年三月广州医学院硕士研究生学位论文结核分枝杆菌常见耐药基因突变的检测与分析Detectionandevalua

结核分枝杆菌耐药性分析及利福平和氧氟沙星耐药基因的检测.docx
结核分枝杆菌耐药性分析及利福平和氧氟沙星耐药基因的检测在全球结核病控制中,耐药性已成为一个主要的挑战。结核分枝杆菌(Mycobacteriumtuberculosis)耐药性是指结核病每种治疗方法对分枝杆菌所产生的抗药性。耐药性的提高增加了治疗难度和费用。因此,对于分枝杆菌耐药性的分析和利福平和氧氟沙星的耐药基因的检测显得尤为重要。本文旨在综述分枝杆菌耐药性及利福平和氧氟沙星耐药基因的检测。1.结核分枝杆菌耐药性分析结核分枝杆菌耐药性分析是指对分枝杆菌对不同抗结核药物的敏感性和抗性状态进行分析和检测。目前

丽水市结核分枝杆菌耐药基因ropB的检测分析.pdf
�414��2010年7月�第32卷第7期�短篇论著�丽水市结核分枝杆菌耐药基因ropB的检测分析雷永良�陈秀英�王晓光�梅建华�兰进权�凡鹏飞�叶碧峰�柳付明�李永芬�叶茂华(丽水市疾病预防控制中心�丽水�323000)��利福平(RFP)是最重要的一线抗结核药物之挑取2~3环菌落于含有500�lTE的1.5ml的一,据报道约90%以上RFP耐药株对异烟肼Eppendorf管中,封口膜封口。在旋涡混合仪震荡,(INH)也耐药,而单耐RFP的菌株很少,故RFP耐混匀菌落,100!干浴30min,12000

结核分枝杆菌异烟肼耐药基因KatG分析.pdf
中国卫生检验杂志2010年6月第20卷第6期ChineseJournalofHealthLaboratoryTechnology,Jun2010;Vol20No61391【微生物检测方法】结核分枝杆菌异烟肼耐药基因KatG分析梅建华,雷永良,王晓光3,陈秀英(浙江省丽水市疾病预防控制中心,浙江丽水323000)[摘要]目的:了解丽水地区结核分枝杆菌耐INH分离株KatG基因突变情况。方法:采用PCR-DNA直接测序法对48株结核分枝杆菌临床分离株KatG基因与耐INH关系密切的突变位点进行分析。结果:药敏
