
基于GrC模型的经颅磁声电刺激对神经元放电活动的影响.docx

快乐****蜜蜂


在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

基于GrC模型的经颅磁声电刺激对神经元放电活动的影响.docx
基于GrC模型的经颅磁声电刺激对神经元放电活动的影响Title:TheImpactofTranscranialMagnetic-Acoustic-ElectricStimulationonNeuronalFiringActivity:AGrCModel-BasedApproachAbstract:Transcranialmagnetic-acoustic-electricstimulation(TMAES)hasemergedasanon-invasivetechniqueformodulatingneu

基于H-H神经元模型的经颅磁声刺激对神经元放电活动的影响.docx
基于H-H神经元模型的经颅磁声刺激对神经元放电活动的影响标题:基于H-H神经元模型的经颅磁声刺激对神经元放电活动的影响摘要:经颅磁声刺激是一种非侵入性的神经调节技术,已在临床上被广泛应用于神经系统相关疾病的治疗和研究。Hodgkin-Huxley(H-H)神经元模型是描述神经元放电活动的经典模型之一。本文通过基于H-H神经元模型的研究,探讨经颅磁声刺激对神经元放电活动的影响,包括刺激参数、刺激位置和刺激时间对神经元放电活动的影响等。结果表明,经颅磁声刺激可以调节神经元放电活动,并在一定程度上改善神经系统相

经颅磁声电刺激下不同类型Izhikevich神经元电耦合模型放电特性研究.pptx
汇报人:/目录01经颅磁声电刺激技术简介神经元电耦合模型放电特性的重要性研究目的和意义02Izhikevich神经元模型的原理和特点不同类型Izhikevich神经元模型的分类和特点神经元电耦合模型的建立和原理03经颅磁声电刺激的原理和特点经颅磁声电刺激对神经元电耦合模型的作用机制经颅磁声电刺激对神经元电耦合模型放电特性的影响04不同类型Izhikevich神经元电耦合模型的放电模式和特点不同类型Izhikevich神经元电耦合模型的放电频率和振幅比较不同类型Izhikevich神经元电耦合模型的放电同步
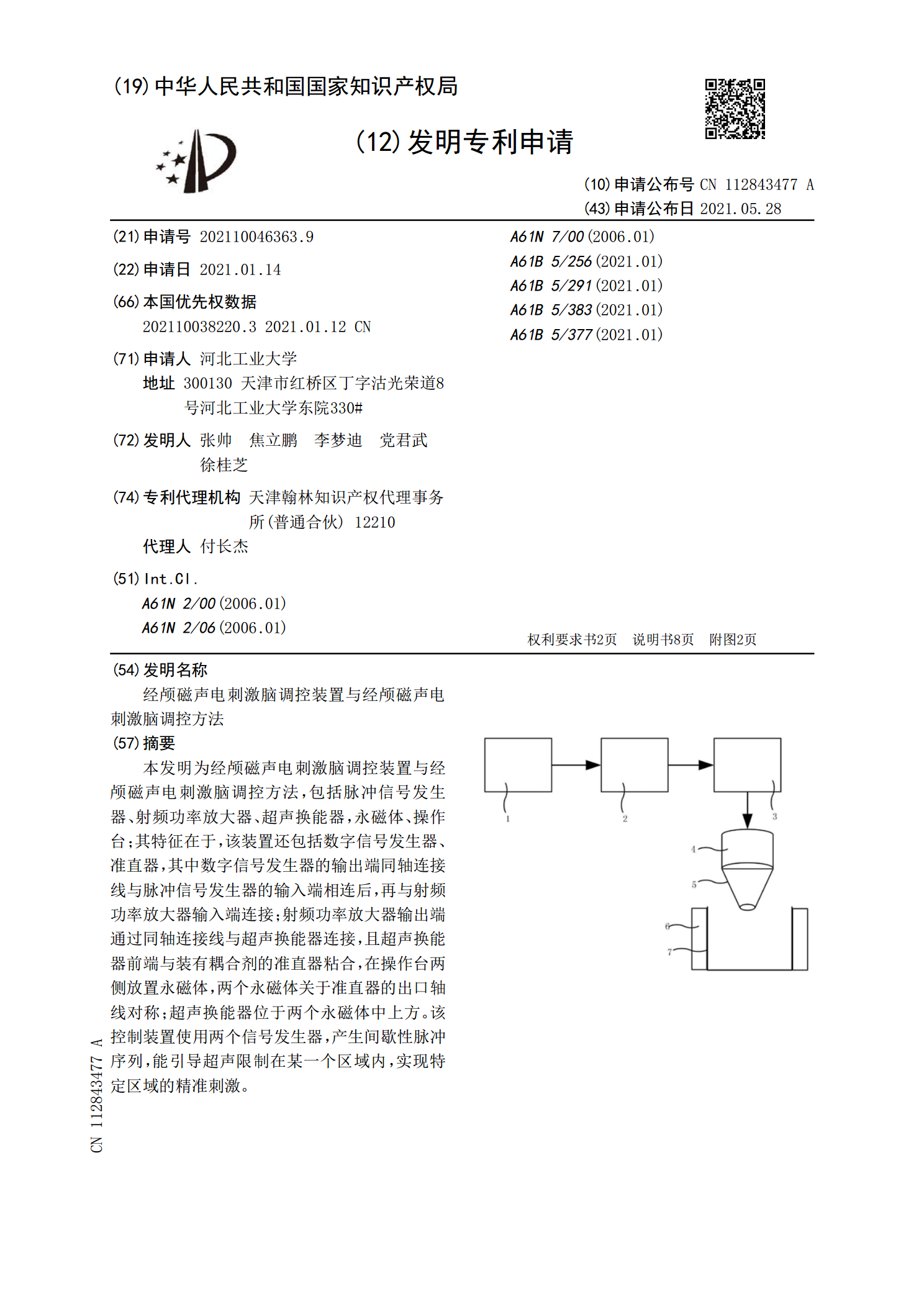
经颅磁声电刺激脑调控装置与经颅磁声电刺激脑调控方法.pdf
本发明为经颅磁声电刺激脑调控装置与经颅磁声电刺激脑调控方法,包括脉冲信号发生器、射频功率放大器、超声换能器,永磁体、操作台;其特征在于,该装置还包括数字信号发生器、准直器,其中数字信号发生器的输出端同轴连接线与脉冲信号发生器的输入端相连后,再与射频功率放大器输入端连接;射频功率放大器输出端通过同轴连接线与超声换能器连接,且超声换能器前端与装有耦合剂的准直器粘合,在操作台两侧放置永磁体,两个永磁体关于准直器的出口轴线对称;超声换能器位于两个永磁体中上方。该控制装置使用两个信号发生器,产生间歇性脉冲序列,能引

基于相控阵聚焦的经颅磁声电刺激仿真与实验分析.pptx
基于相控阵聚焦的经颅磁声电刺激仿真与实验分析目录添加章节标题相控阵聚焦技术相控阵聚焦技术的原理相控阵聚焦技术在经颅磁声电刺激中的应用相控阵聚焦技术的优势与挑战经颅磁声电刺激仿真分析经颅磁声电刺激的原理及作用仿真模型的建立与验证仿真结果的分析与讨论实验设计与实施实验目标与方案实验设备与材料实验过程与步骤实验结果的分析与讨论结果比较与讨论仿真结果与实验结果的比较结果差异的原因分析对未来研究的建议与展望结论总结研究成果的总结对实际应用的建议与展望THANKYOU
