
森林生态系统碳蓄积与碳循环.pdf

yy****24





在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

森林生态系统碳蓄积与碳循环.pdf
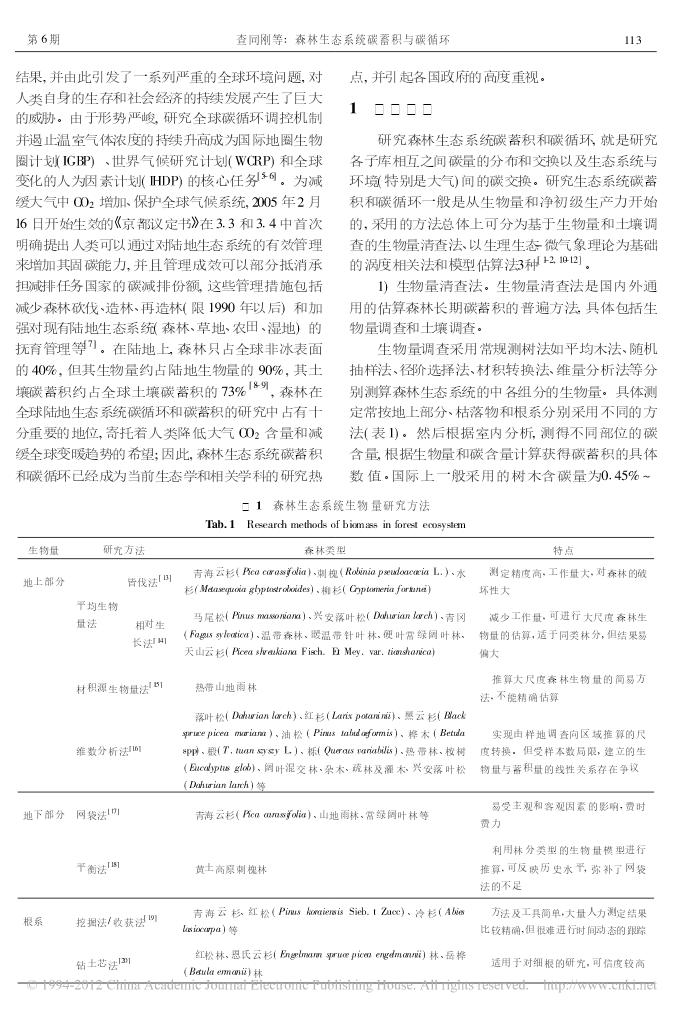
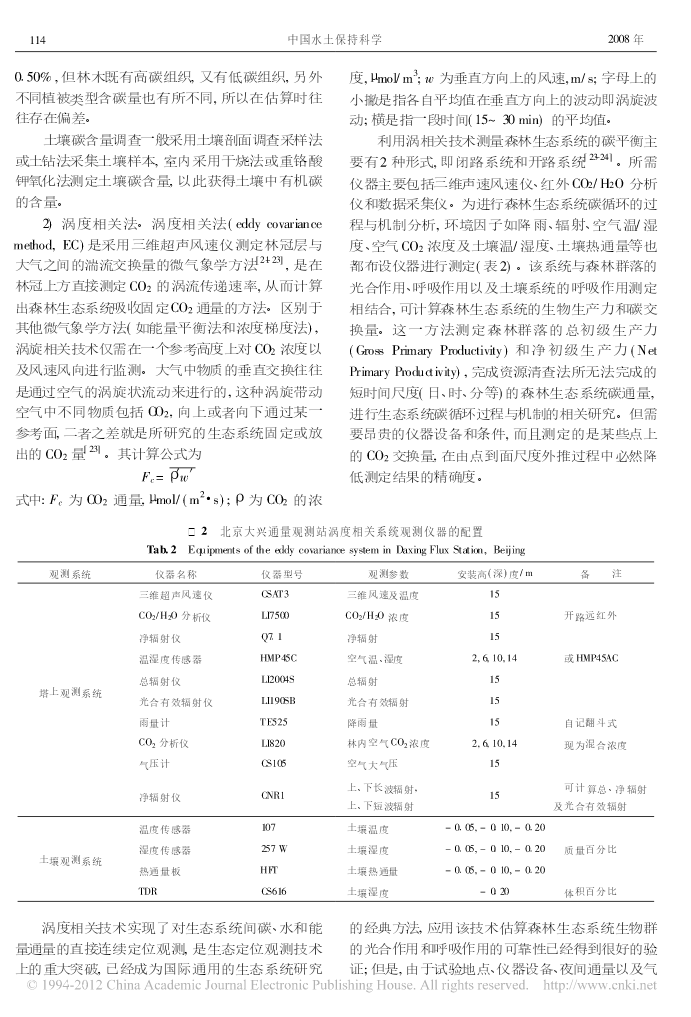
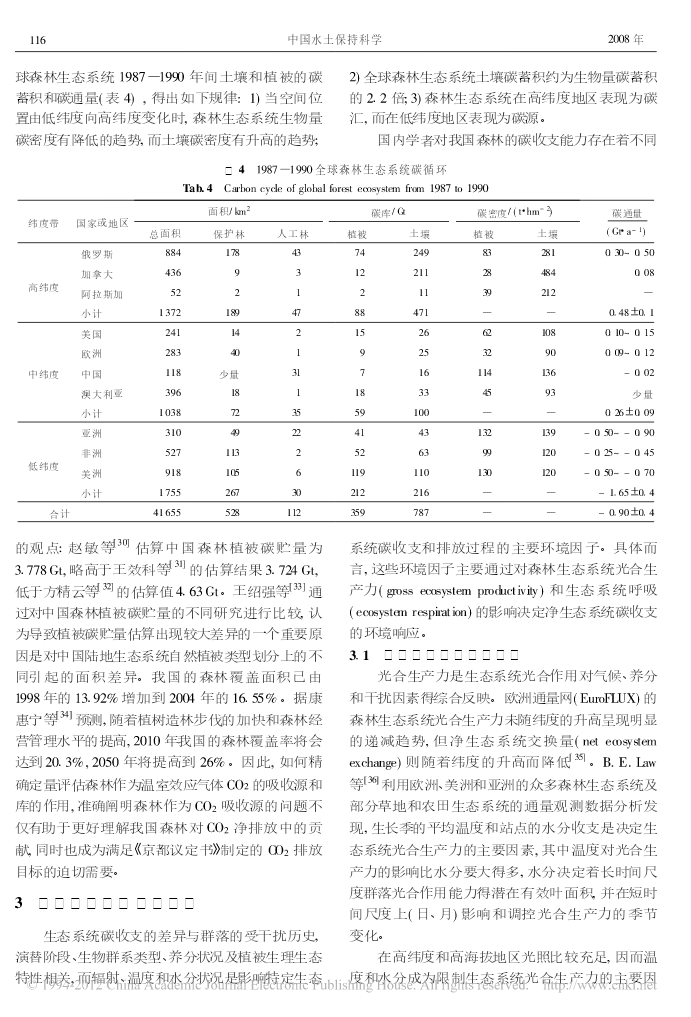
2008年12月中国水土保持科学Vol.6No.66(6):112-119ScienceofSoilandWaterConservationDec.2008森林生态系统碳蓄积与碳循环查同刚1,2,张志强1,2,朱金兆1,2,崔令军1,张津林1,陈军1,谭炯锐1,方显瑞1(11北京林业大学水土保持学院;21水土保持与荒漠化防治教育部重点实验室:100083,北京)摘要通过系统论述森林生态系统碳蓄积与碳循环的研究方法、森林生态系统碳蓄积与碳循环过程的时空特征以及森林与大气间碳交换的环境响应机制,发现:生物量法

森林生态系统在碳循环中的作用.pdf
森林生态系统在碳循环中的作用摘要:本文描述了碳循环及其过程以及森林生态系统的碳循环及其在全球碳循环中的作用,说明了森林生态系统在碳循环中的作用主要取决于森林生态系统的生物量、林产品、植物枯枝落叶和根系碎屑以及森林土壤。关键字:碳循环的过程森林生态系统森林生态系统在碳循环中的作用一、碳循环地球上有五个碳库,最大的两个碳库是岩石圈和化石燃料,但是这两个库中的碳活动缓慢,实际上起着贮存库的作用。还有三个碳库:大气圈库、水圈库和生物库。这三个库中的碳在生物和无机环境之间迅速交换,容量小而活跃,起着交换库的作用。碳

湿地生态系统碳储量与碳循环研究.docx
湿地生态系统碳储量与碳循环研究摘要:湿地作为一个独特的生态系统,具有很高的生态价值。本文主要讨论湿地生态系统在碳储量和碳循环方面的研究以及其对全球碳循环的影响。本文将探讨湿地生态系统中生物和非生物碳的来源、转化和储存过程。研究还将讨论湿地生态系统中各种活动和人类活动对其碳循环的影响。最后,本文将探讨湿地生态系统的保护和管理策略,以维护其生态系统功能和生态系统服务。关键词:湿地,生态系统,碳储量,碳循环,生态系统服务引言:湿地是一个在陆地与水体交界的生态系统,具有极高的生态价值。它们覆盖了全球很大部分面积,

氮沉降对森林生态系统碳循环影响的模拟研究的开题报告.docx
氮沉降对森林生态系统碳循环影响的模拟研究的开题报告一、选题的背景和意义氮沉降是指大气中氮化物沉降到地表的过程,主要来源于化石燃料的燃烧、农业、工业及交通活动等人类活动。长期以来,氮沉降已经成为全球环境问题的关注焦点之一。氮沉降不仅对土壤和水环境产生影响,也对森林生态系统的生态功能造成了一定的影响。森林生态系统是地球生态系统的重要组成部分,对全球生态环境和碳循环过程具有重要的作用。氮沉降对森林生态系统的生态功能和碳循环影响的研究具有重要意义。在全球气候变化的背景下,探究氮沉降对森林生态系统的影响,有助于加深

碳同位素在草地生态系统碳循环中的应用与展望.docx
碳同位素在草地生态系统碳循环中的应用与展望随着全球气候变化和温室效应的日益加剧,碳循环已成为生态学和环境科学领域研究的热点话题。碳同位素技术以其高精度、高灵敏度的特点,在生态系统碳循环领域中得到了广泛的应用。本文将以草地生态系统为例,探讨碳同位素在草地生态系统碳循环中的应用及其展望。草地生态系统的碳循环是指通过植物光合作用将二氧化碳转化为有机碳的过程,以及有机碳在生物圈、大气圈和地球圈之间的交换和转移过程。草地生态系统中碳的循环过程对于了解全球碳循环和全球气候变化具有重要意义。因此,碳同位素技术成为了研究
