
武汉典型湖泊沉积物中重金属累积特征及其环境风险.pdf

瀚玥****魔王





在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

武汉典型湖泊沉积物中重金属累积特征及其环境风险.pdf
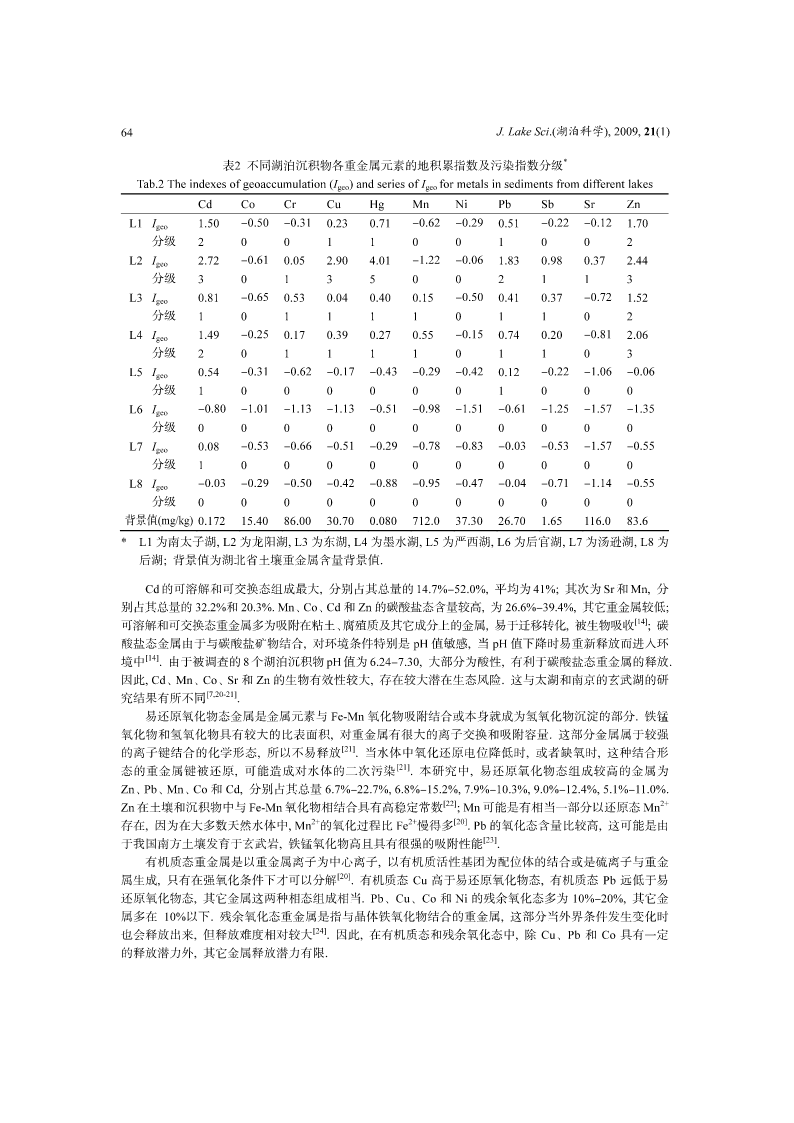
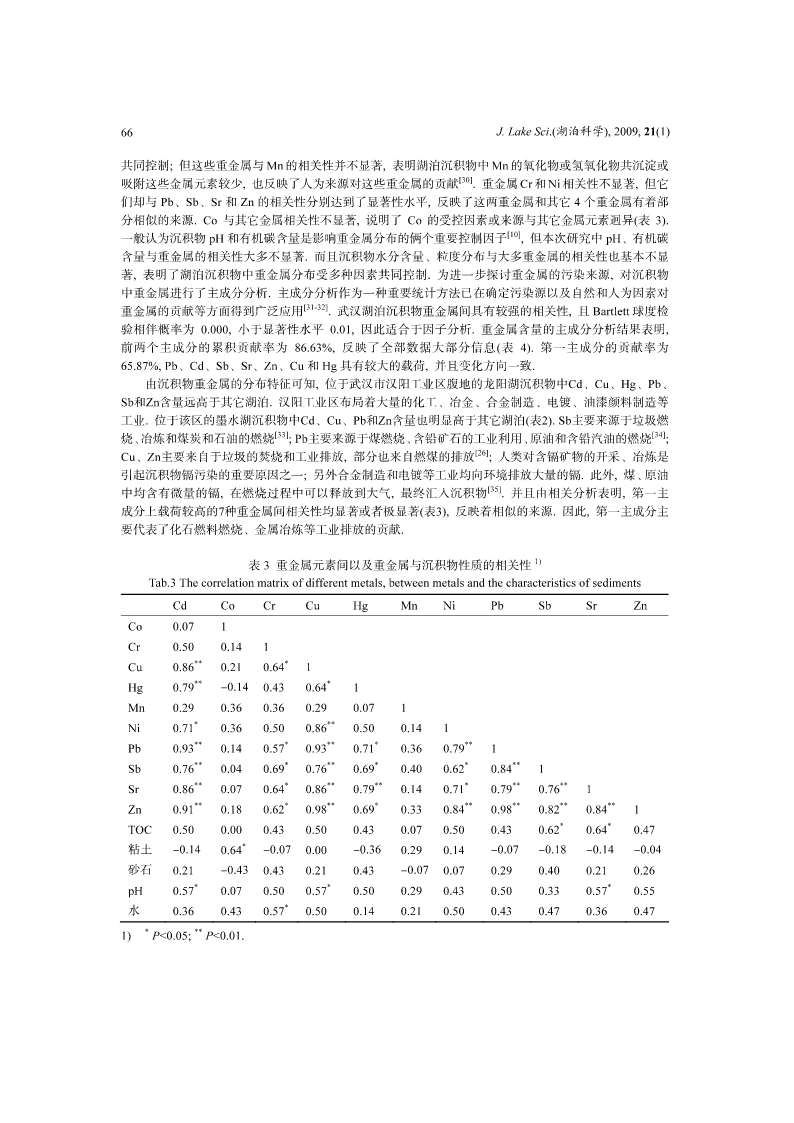
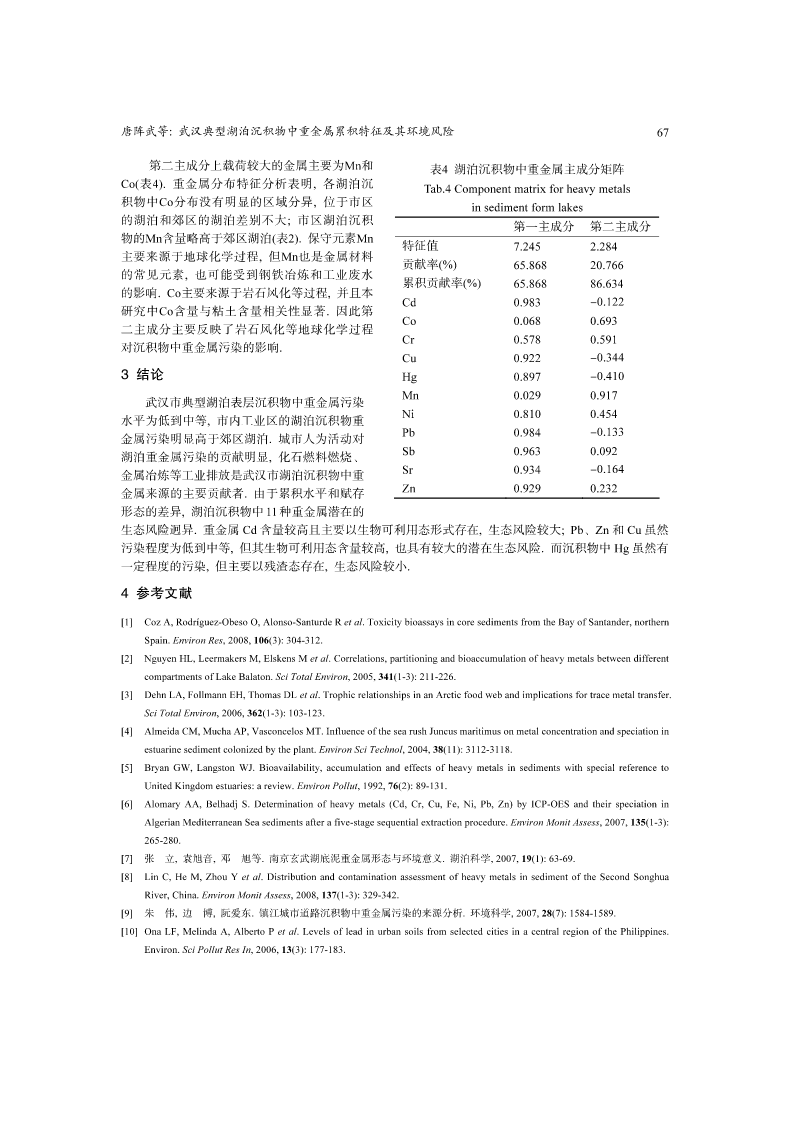
J.LakeSci.(湖泊科学),2009,21(1):61-68http://www.jlakes.org.E-mail:jlakes@niglas.ac.cn©2009byJournalofLakeSciences武汉典型湖泊沉积物中重金属累积特征及其环境风险*唐阵武1,2,程家丽1,岳勇2,3,陈玉敏2(1:华北电力大学能源与环境研究中心,北京102206)(2:水环境模拟国家重点实验室,北京师范大学环境学院,北京100875)(3:中国石油集团安全环保技术研究院,北京100083)摘要:采集武汉市

城市湖泊表层沉积物中的重金属污染现状及其风险评价――以武汉墨水.pdf

基于地累积向量模型的湖泊沉积物重金属污染评价.docx
基于地累积向量模型的湖泊沉积物重金属污染评价基于地累积向量模型的湖泊沉积物重金属污染评价摘要:湖泊沉积物是环境重金属污染的主要记录,对湖泊沉积物中重金属的精确评价具有重要科学意义。本研究以地累积向量模型为基础,通过分析湖泊沉积物重金属元素及其组合的空间分布特征,对湖泊沉积物的重金属污染进行评价。结果表明,地累积向量模型能够有效评价湖泊沉积物中重金属的污染程度,并为进一步研究湖泊环境质量提供科学依据。关键词:湖泊沉积物;重金属污染;地累积向量模型1.引言湖泊是重要的地表水体,对人类和生态系统具有重要意义。然

风力影响下湖泊湍流特征及其对湖泊污染沉积物影响研究.pptx
添加副标题目录PART01PART02风力作用下湖泊水体的流动状态湍流参数的测量和计算方法风力强度与湍流特征的关系不同湖泊类型对湍流特征的影响PART03湖泊沉积物的污染来源风力对沉积物迁移的影响沉积物中污染物的扩散与释放风力作用下的沉积物污染风险评估PART04沉积物的粒径和组成沉积物中有机质和重金属的含量沉积物的酸碱性和氧化还原电位沉积物的吸附和解吸性能PART05沉积物中微生物的群落结构和功能风力对沉积物中污染物降解的影响沉积物对水生生物的毒性效应风力作用下的生物修复技术探讨PART06湖泊环境保护

典型杀生剂在我国湖泊沉积物中的污染特征、生态风险及微生物降解行为.docx
典型杀生剂在我国湖泊沉积物中的污染特征、生态风险及微生物降解行为典型杀生剂在我国湖泊沉积物中的污染特征、生态风险及微生物降解行为摘要:典型杀生剂作为一类常见的农药,其在农业生产中的广泛应用导致了环境中的污染。湖泊作为重要的水域生态系统,是典型杀生剂的潜在“汇聚区”。本文主要探讨了典型杀生剂在我国湖泊沉积物中的污染特征、生态风险及微生物降解行为。通过分析现有研究,了解了湖泊沉积物中典型杀生剂的主要污染特征、对湖泊生态系统的潜在风险以及微生物降解在降低典型杀生剂污染的重要作用。关键词:典型杀生剂;湖泊沉积物;
