
碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料湿热残余应力的微Raman光.pdf

qw****27



在线预览结束,喜欢就下载吧,查找使用更方便
相关资料

碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料湿热残余应力的微Raman光.pdf
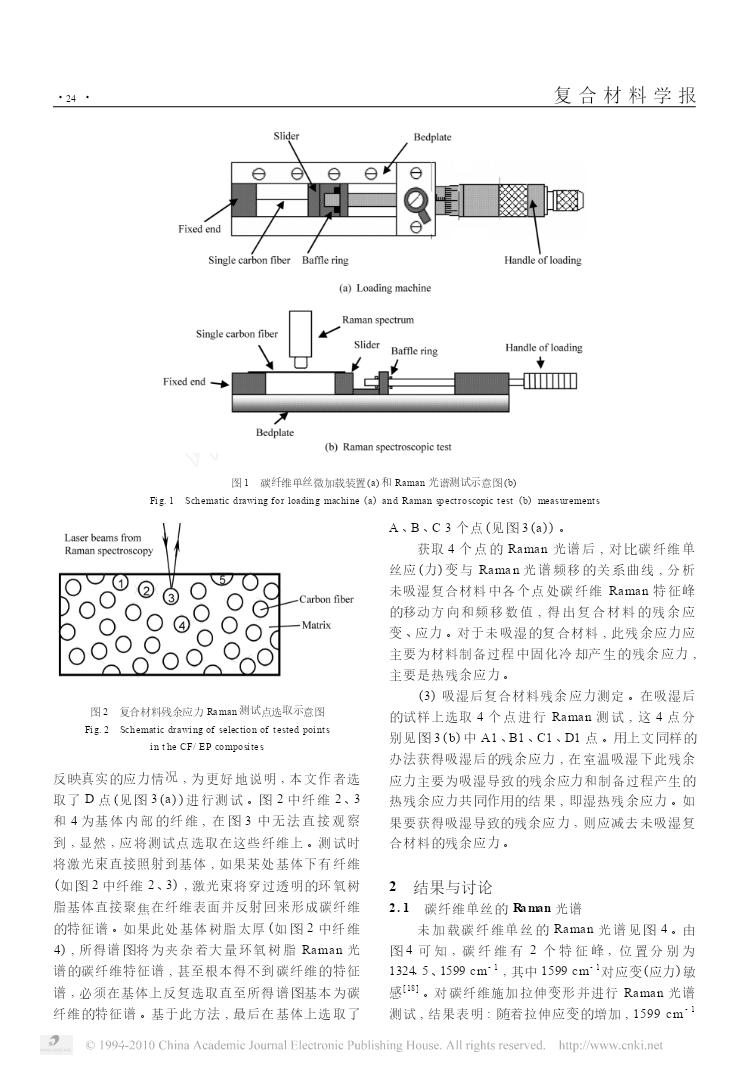
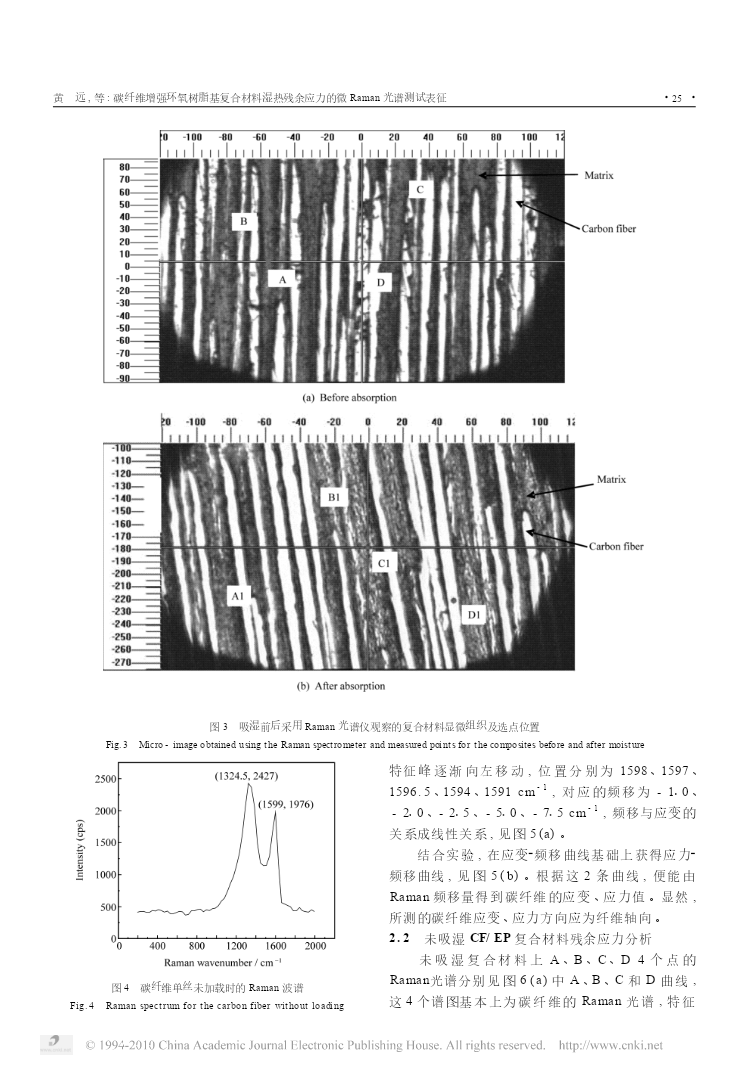
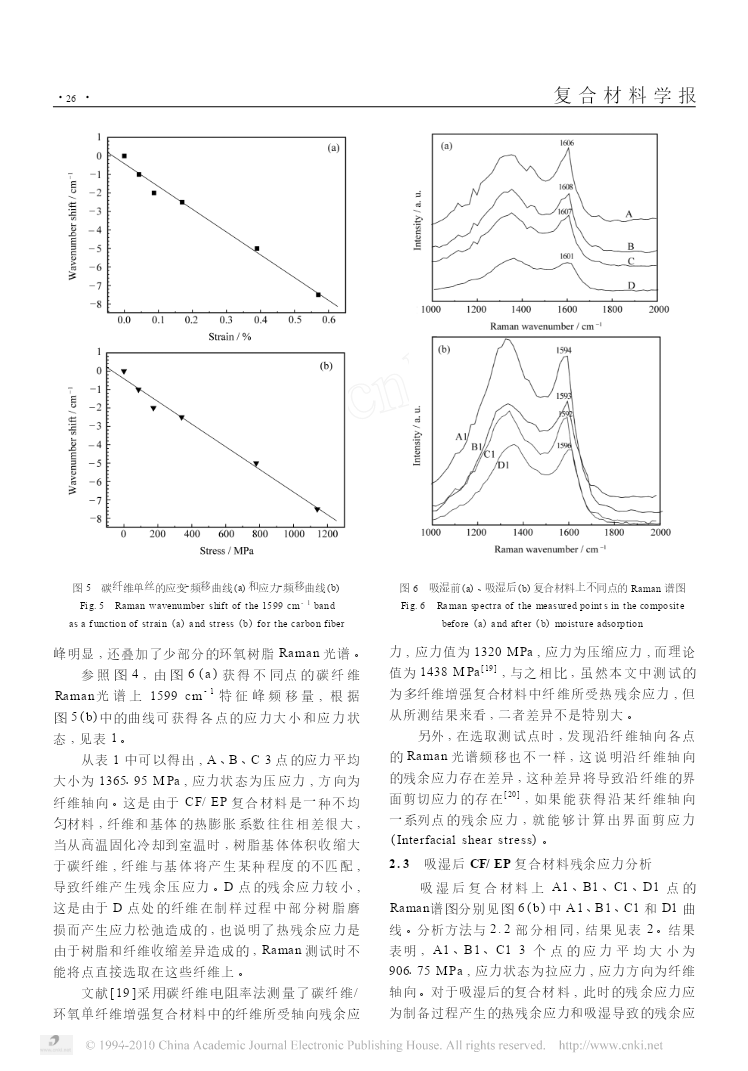
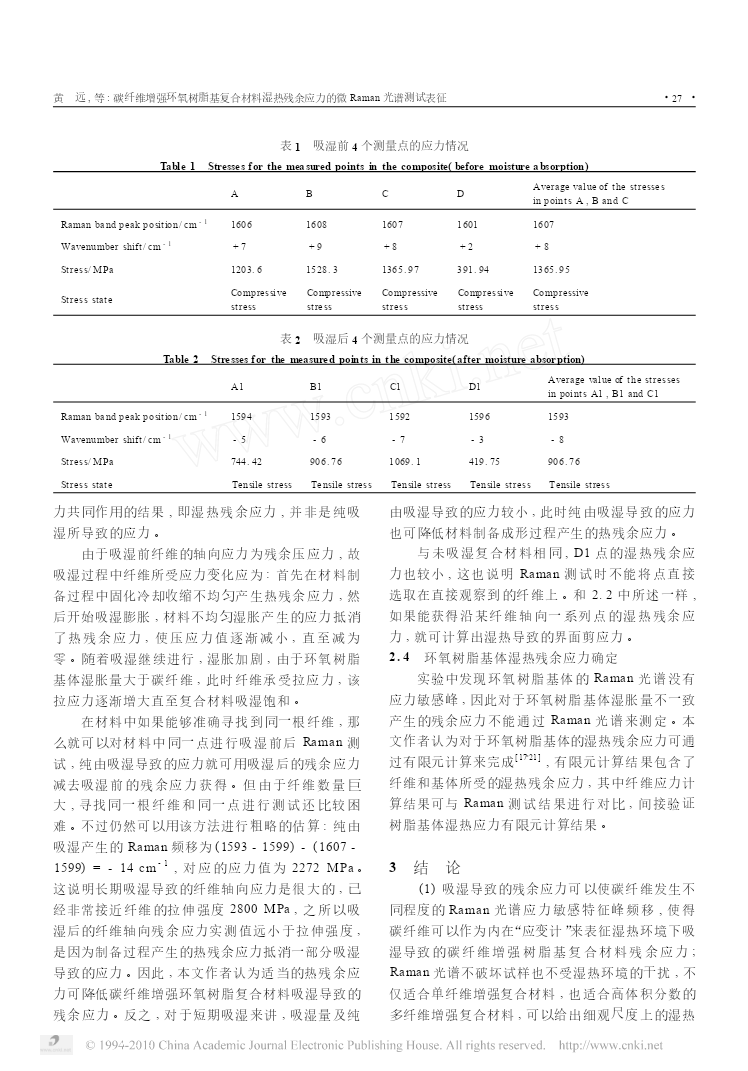
复合材料学报第26卷第4期8月2009年ActaMateriaeCompositaeSinicaVol126No14August2009文章编号:100023851(2009)0420022207碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料湿热残余应力的微Raman光谱测试表征黄远3,何芳,万怡灶,王玉林,李刚,高智芳(天津大学材料科学与工程学院,天津300072)摘要:采用微Raman光谱仪对碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料CF/EP(纤维体积分数为30%)的湿热残余应力进行了研究。实验结果表明:湿热残余应力能够使碳纤维Ra

碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料的性能研究.pdf
2009年3月第18卷第3期中国胶粘剂V01.18No.3.Mar.2009CHINAADHESIVES21碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料的性能研究张杰,宁荣昌,李红,齐大伟,凌辉(西北工业大学应用化学系,陕西西安710129)摘要:研究了WBS一3环氧树脂固化体系的反应特性,分析了该固化体系浇铸体的性能;并以碳纤维(T一700S)为增强材料,采用手糊成型螺栓加压工艺制备了WBS-31T-700S复合材料,研究了复合材料的常温力学性能、高温力学性能、水煮后力学性能和动态力学性能,并对弯曲断面进行分析。研究结

碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料研究进.ppt
碳纤维增强耐热环氧树脂基复合材料材料组成碳纤维表面处理表面处理方法在较低温度下,稀释剂对黏度降低有较大贡献,随温度的升高,稀释剂的作用逐渐减弱。图2是树脂体系在室温和50下黏度随时间的变化。在室温下树脂体系的黏度变化很小,经过35h后从300mPas,升高到450mPas,,适用期较长;在50下,10h后树脂黏度升高很快,但15h内黏度也小于500mPas,,可以满足RTM工艺要求。复合材料的性能研究结论2011.01.13航天飞机雷达罩1LuYao,DuanYuexin,LiangZhiyong.Stu

碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料湿热老化研究进展.docx
碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料湿热老化研究进展碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料是一种具有优异性能的材料,广泛应用于航空航天、汽车、体育器材等领域。然而,长期暴露在湿热环境下的复合材料会受到湿热老化的影响,使其力学性能、耐久性和可靠性下降。因此,研究碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料的湿热老化行为对于提高复合材料的性能,延长其使用寿命具有重要意义。湿热老化是指材料在高温和湿度的作用下,其性能逐渐发生变化的过程。湿热环境中,水分子会渗透进树脂基质中,导致树脂基质的酯键断裂,从而引起材料的颜色变化、重量损失、尺寸变化和性能下降。此外,

碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料应用研究.docx
碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料应用研究碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料应用研究摘要:随着环境保护意识的提高和可降解材料的需求增加,碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料作为具有优异性能和环境友好的新型材料受到了广泛的关注和研究。本文综述了碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料的制备方法、性能及其在不同领域的应用。研究表明碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料具有良好的力学性能、高温性能、耐腐蚀性能和可降解性能,适用于航空航天、汽车制造、建筑工程和医疗领域等多个领域。然而,碳纤维增强可降解环氧树脂基复合材料制备过
